How to setup microservices in gae as cheaply as possible

Summary
This tutorial will cover how to make microservices in google app engine using google cloud build. This is intended to only provide a boilerplate for microservices with google cloud platform and not a description of how to code a REST api.
Before we can begin making microservices, we need to enable the google app engine api for the given project. If you dont have an account, you can sign up for a free trial at google cloud. After creating a project we need to
- enable the api app engine in google cloud platform for the given project
- create an app engine project
- give default cloud build service permission to deploy to app engine
Enabling App Engine Api
The url is at, remember to replace project_id with your google cloud platform project.
https://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/appengine.googleapis.com/overview?project=${project_id}
After enabling the api we need to create an google app engine application.
Creating app engine application
If you already have an app engine application, you can skip this step.
- Go to the sidebar and find -> App Engine -> Create application.
- You can ignore the get started prompt.
After creating an app engine application, we need to update the default google cloud service account to have access to google app engine.
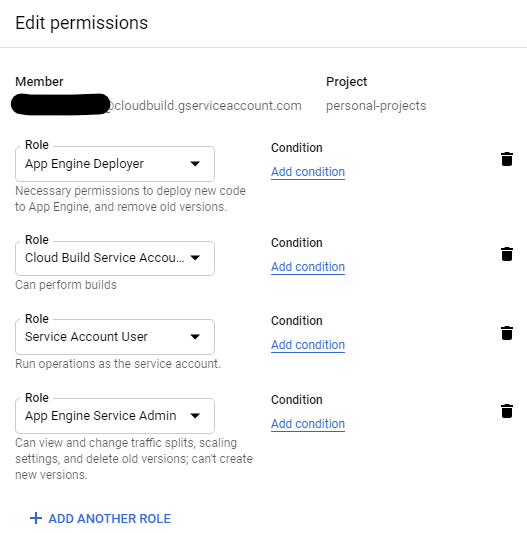
Updating cloud build permissions
The default Cloud Build service account does not allow access to deploy App Engine. You need to enable the Cloud Build service account to perform actions such as deploy.
The Cloud Build service account is formatted like this:
[PROJECT_NUMBER]@cloudbuild.gserviceaccount.com
- Go to the Google Cloud Console -> IAM & admin -> IAM.
- Locate the service account and click the pencil icon.
- Add the role “App Engine Deployer” and “Service Account User” to the service account.
Wait a couple of minutes for the service account to update globally and then try again.
For simplicity, I have copied the boilerplate for the google app engine fastapi.
The contents of main.py as is follows.
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
# domain where this api is hosted for example : localhost:5000/docs to see swagger documentation automagically generated.
@app.get("/")
def home():
return {"message": "Hello TutLinks.com"}To deploy this application to google cloud platform we have a simple fastapi.yaml file to configure the version of python and the start command. The url for the api microservice will be prepended with api-dot.
service: api
runtime: python37
basic_scaling:
max_instances: 1
idle_timeout: 10m
resources:
cpu: 1
memory_gb: 1
disk_size_gb: 1
entrypoint: gunicorn -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker pyfastapi:appBasic scaling can be changed as needed, these are the defaults that works for me.
steps:
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
id: deploy_go
args: ["app", "deploy", "goapp.yaml"]
timeout: "600s"
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
id: deploy_dash
args: ["app", "deploy", "fastapi.yaml"]
timeout: "600s"
dir: python/apiThis will build the default app service and the fast api service in the python/api directory. Each push will make a new version in app engine. Personally, I do not feel the need to delete old app versions at the moment.
Another useful step that runs is the cleanup stage. To decrease build times and a bunch of old docker images that are no longer needed. This is just a personal preference to pay no money to google.
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud'
entrypoint: bash
id: cleanup2
args:
- '-c'
- |
now=$(date --date="next Friday" +"%Y-%m-%d")
chmod +x gcrgc.sh
./gcrgc.sh us.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app-engine-tmp/build-cache/ttl-7d/python-cache $now
./gcrgc.sh us.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app-engine-tmp/app/ttl-2h $now
waitFor:
- deploy_dash
- deploy_api
dir: scriptsIf the google cloud build is successfully, congratulations, you have successfully deployed microservices to google app engine.
For the full source code, you can visit github.